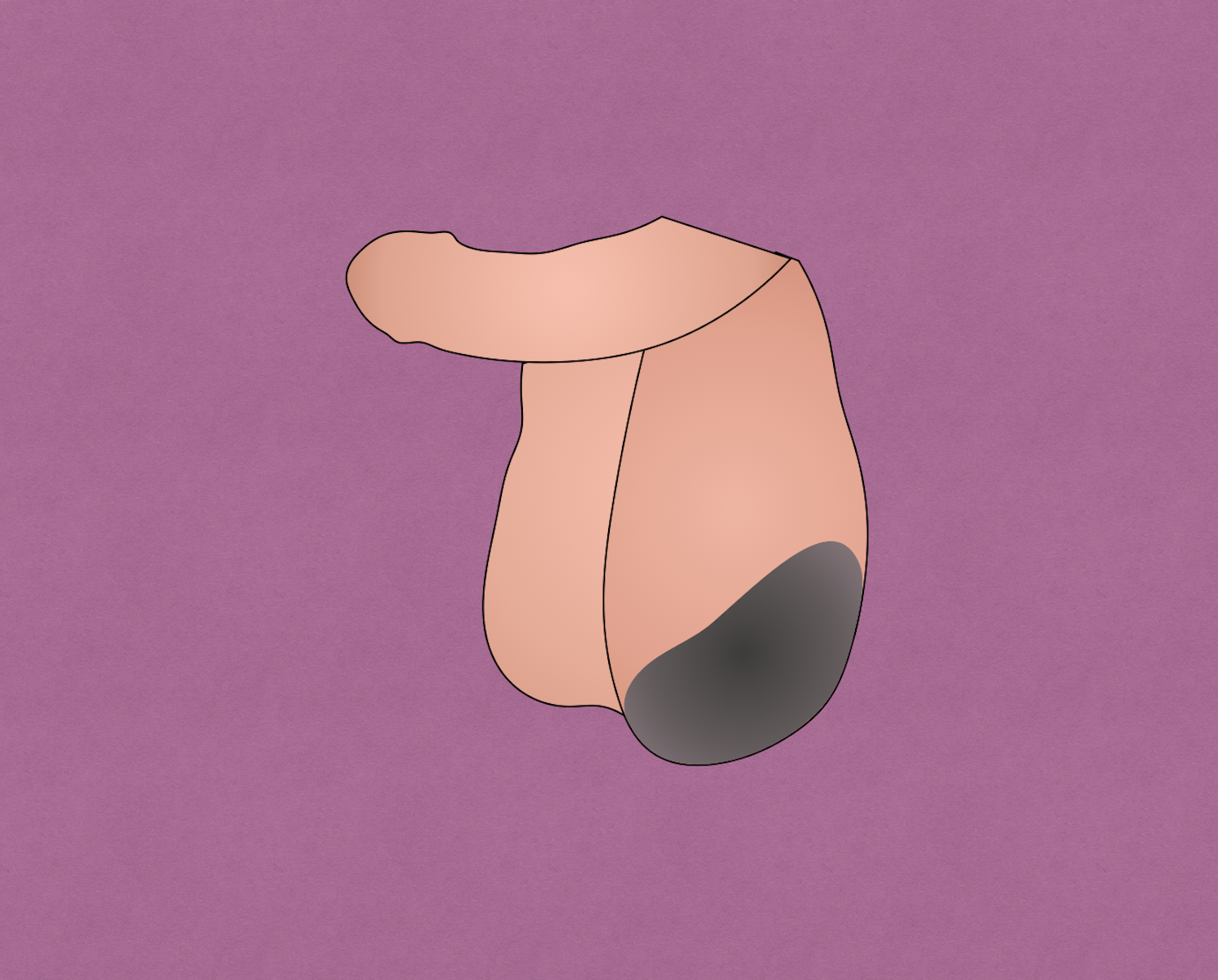
Fournier gangrene is a fulminant form of necrotizing fasciitis that affects the perineal, genital, or perianal regions. It was first described in 1883 by Alfred Fournier, a French dermatologist and venereal specialist.
Etiology
- Risk factors: diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, chronic alcohol abuse, immunosuppression, malnutrition
Epidemiology
- Elderly males (most common)
- Can occur in females and children
Pathogenesis
- Usually begins with a bacterial infection
- Often mixed → aerobic/anaerobic
- Commonly grow Klebsiella, streptococci, staphylococci, clostridia, Bacteroides, and corynebacteria
- Microthrombosis of small subcutaneous vessel occurs which leads to gangrene of the skin overlying this region
Physical Exam
- Pain, tenderness, erythema, and swelling of affected site – perineal, genital, or perianal region
- Foul smelling discharge
- Crepitus (due to gas forming organisms)
- Necrotic patches on overlying skin as condition progresses and inflammation continues to increase
Labs
- CBC: elevated WBC
- CMP: hyponatremia, metabolic acidosis, concurrent renal failure
- Serum lactate
- CRP
- Procalcitonin
- ABGs
- HbA1c
- Blood culture
- Wound culture
Imaging
- US → subcutaneous gas, cobblestoning (individual subcutaneous fat globules surrounded by fluid), snow globe effect (swirling appearance of heterogenous subcutaneous material)
- X-ray → subcutaneous gas following fascial plane
- CT → fat stranding, subcutaneous emphysema, abscess, asymmetric fascial thickening
- MRI is not recommended for initial diagnosis
Treatment
- Surgical emergency! Progresses rapidly and can lead to sepsis with multiple organ failure and death.
- Surgical debridement → often three to four operations before total debridement is complete
- Urinary or fecal diversion if necessary. Often unnecessary at initial debridement.
- Closing surgical site
- Vacuum-assisted closure system dressings help with closing and accelerate healing
- Split thickness skin grafts are the primary choice in covering perineal and scrotal skin defects
- Hemodynamic stabilization
- Broad-spectrum IV antibiotics
Relevant Information
- Can extend to involve different regions of the body depending on the initial site of infection. Since the blood supply of the testes originates intraabdominally, they are usually spared.
Complications
- Acute renal failure
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Heart failure
- Multiple organ failure
- Bacteremia
- Incontinence
Differential Diagnoses
- Cellulitis
- Chancre
- Epididymitis
- Orchitis
- Pyonephrosis
- Scrotal abscess
- Scrotal edema
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Testicular torsion
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Vasculitis