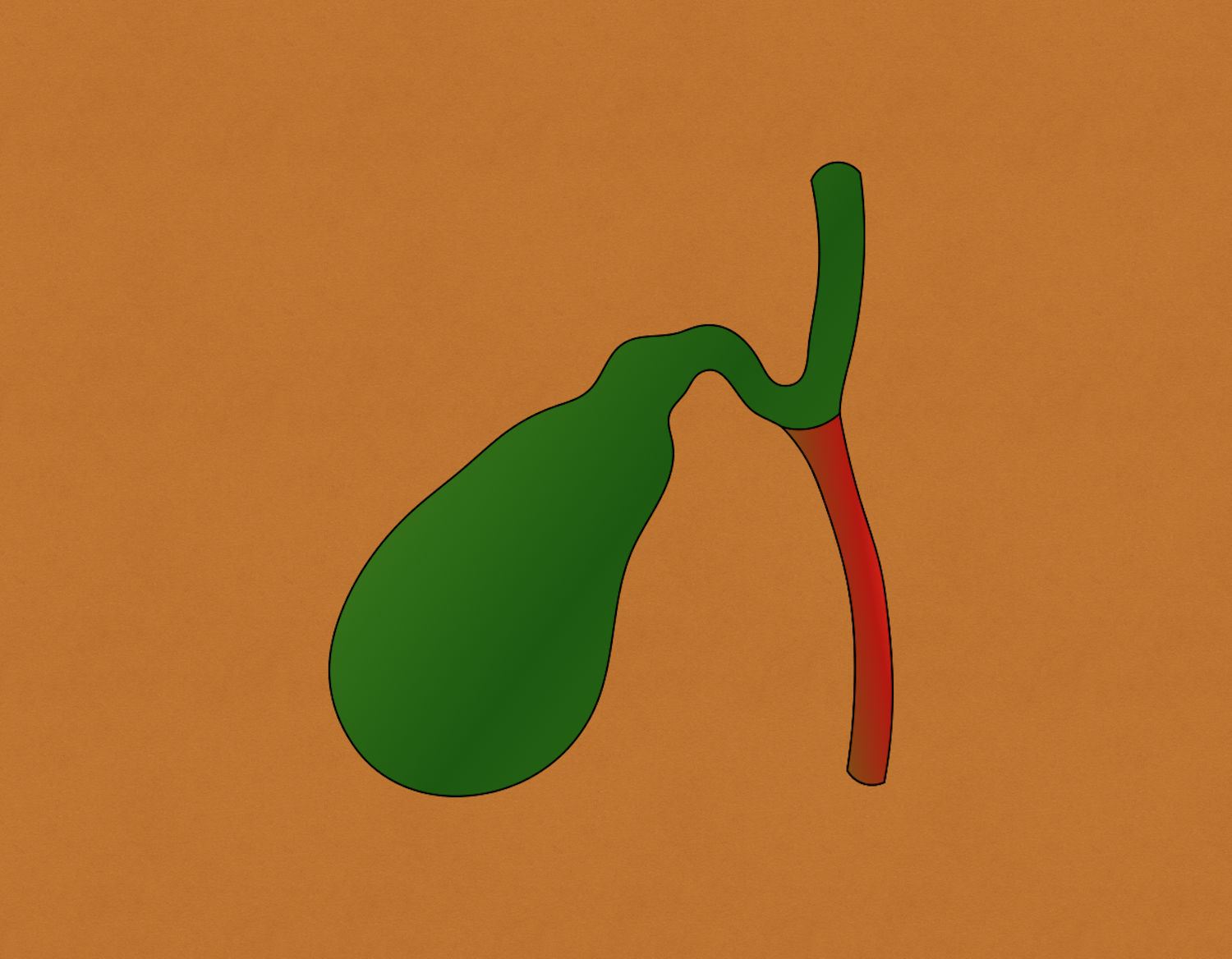
Cholangitis is an ascending infection of the common bile duct (CBD) secondary to obstruction and increased intraluminal pressure. It was first described in 1877 by Jean-Martin Charcot.
Etiology
- MCC: choledocholithiasis
- Benign or malignant stricture of bile duct or hepatic ducts
- Pancreatic cancer
- Ampullary adenoma or cancer
- Porta hepatitis tumor or metastasis
- Biliary stent obstruction
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis
- Amyloid deposition in biliary system
- Parasites
- Mirizzi syndrome
- Lemmel syndrome
- AIDS
Epidemiology
- Uncommon
- Equal distribution between males and females
History
- Charcot’s triad: RUQ pain, fever, jaundice (rarely presents with all three)
- May progress to septic shock and present with Reynold’s pentad
- Reynold’s pentad: Charcot’s triad, altered mental status, hypotension
Imaging
- US
- Findings: thickening of the walls of the bile duct, dilatation of biliary ducts (including the CBD), evidence of cholelithiasis and pyogenic material
- CT
- Can be performed a adjunct to investigate coexisting pathologies
- May help with differential diagnoses
- Poor sensitivity for choledocholithiasis
- Often needed to aid in diagnosis and in identifying sources of obstruction
Treatment
- Emergent, life-threatening condition!
- IVF
- IV antibiotics: directed towards enteric pathogens (such as fluoroquinolones, extended-spectrum penicillins, carbapenems, and aminoglycosides)
- Biliary drainage
- Indicated if patient is severely ill with sepsis
- ERCP
- Gold standard, treatment of choice
- Effective 94 – 98% of the time
- Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC)
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
- Surgical drainage via cholecystectomy
Relevant Information
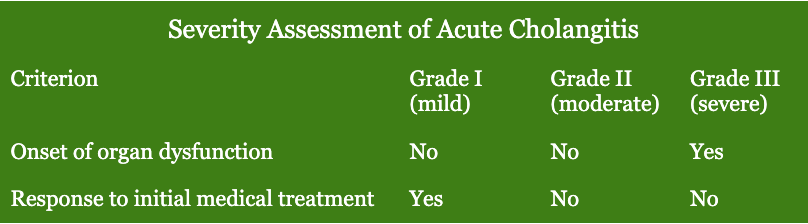
Complications
- Hepatic abscess
- Acute cholecystitis
- Portal vein thrombosis
- Acute biliary pancreatitis
- Liver failure
- Acute renal failure
- Bacteremia/septicemia
- Multiple organ failure
Differential Diagnoses
- Acute cholecystitis
- Cirrhosis of liver
- Acute hepatitis
- Liver abscess
- Septic shock
- Right-sided diverticulitis
- Right-sided pyelonephritis